Quantile UQNet, A Conformal, Nonlinear Scaling Model for Uncertainty Prediction
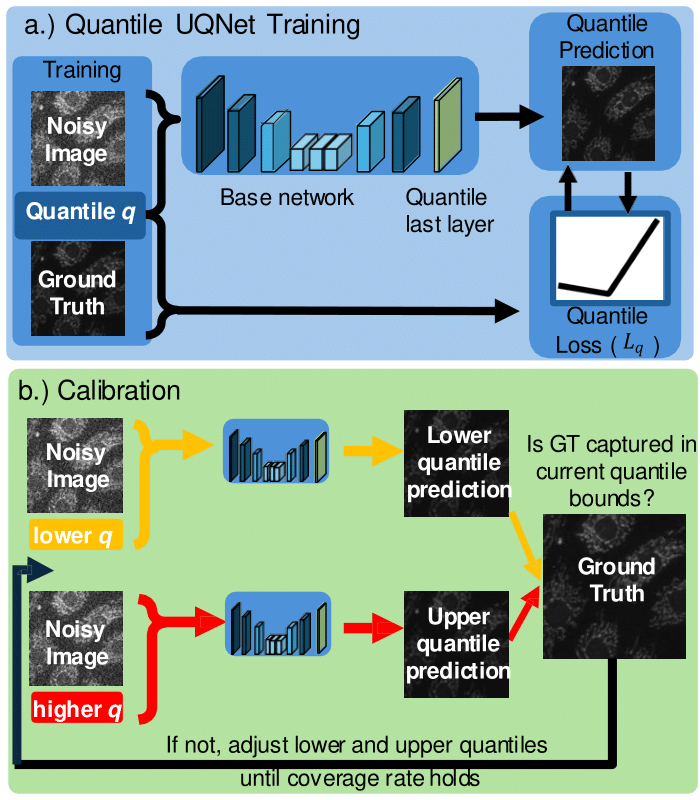
Abstract: Deep learning models hallucinate and for scientific applications such as biomedical image denoising, predictions that deviate from the ground truth can have catastrophic downstream effects. Uncertainty quantification techniques can improve the reliability of deep learning models by detecting hallucinations and improving prediction confidence. We propose Quantile UQNet, a conformal network that provides a more accurate estimate of uncertainty than previous networks. To achieve this, our model applies a nonlinear scaling to its predictions, ensuring a tighter and more reliable bound on uncertainty estimates. We test this network on Gaussian image denoising and demonstrate its ability to provide meaningful uncertainty predictions that are independent of the signal in the sample. Compared to the method introduced in Image-to-Image regression, our model consistently achieves better denoising performance and smaller uncertainty intervals, while maintaining the same statistical coverage.
Paper: Quantile UQNet: A Conformal, Nonlinear Scaling Model for Uncertainty Prediction
Poster presented in CVPR UnCV (Spotlight), 2025.